Your body is always swapping and mending free-radical damaged cells; but with the way we live and mistreat ourselves, our bodies are attacked with more free radicals than they can handle.
By choosing to supplement with antioxidants, we help our bodies keep up with the carnage. What’s more, it’s possible to get ahead of the game and reverse some of that harmful effect.
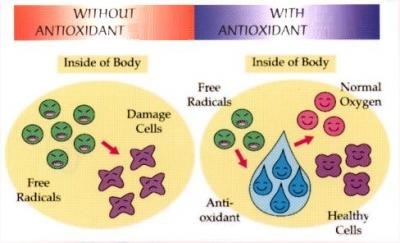
Antioxidants come up regularly in discussions about wellbeing and avoiding diseases. These potent elements, which mostly come from the fresh fruits and vegetables we consume, forbid (and in some cases even inhibit), the oxidation of other molecules in the body. The advantages of antioxidants are quite significant to good health, because if free radicals are left unrestrained, they can cause a wide range of sicknesses and long-lasting illnesses. Antioxidants help the body by deactivating and eliminating the free radicals from our circulatory system.
Dr. Denham Harman suggested this theory back in 1954. It was a radical theory (punny, I know) back in those days and pretty much disregarded until the late 1960’s, when a few scientific studies verified his claim. Ever since, over 80 degenerative ailments have been linked to the consequences of oxidative stress (that’s what they call the damage from free radicals).
 Scientists now assume that all these degenerative diseases are not really isolated things after all. They’re just the diverse ways your body expresses the results of the impairment it has suffered.
Scientists now assume that all these degenerative diseases are not really isolated things after all. They’re just the diverse ways your body expresses the results of the impairment it has suffered.
Basically, in whichever area the free radical damage happens the most decides what disease you’ll get. If there’s more free radical damage in your blood vessels, you’ll get heart disease. In your eyes? Cataracts. In your brain? Dementia or Alzheimer’s. If there’s more in your breast tissue, you’ll get breast cancer. And so on and so forth…
Every year now there are more and more scientific studies demonstrating the tie between antioxidants and disease. For better understanding the general health benefits of antioxidants I recommend to check out: Classification of Antioxidants based on How They Work and What Other Roles Do Antioxidants Play In Our Body?
Some of the pros of consuming antioxidant rich foods include:
- Slower Aging
- Healthy Glowing Skin
- Reduce Cancer Risk
- Reduce Inflammation
- Detoxification Support
- Longer Life Span
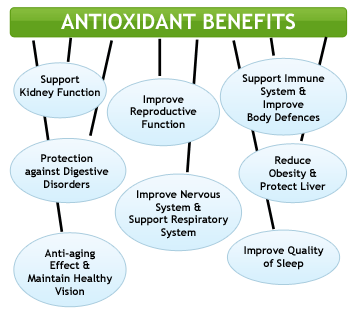
Different Antioxidants Benefit Different Parts of the Body
There are a wide range of antioxidants found in nature, and because they are so diverse, various antioxidants provide benefits to various parts of the body. For example, beta-carotene (and other carotenoids) is very useful to aid eye health; lycopene is beneficial for helping conserve prostate health; flavonoids are particularly valuable for heart health; and proanthocyanidins are helpful for urinary tract health.
But consider this: antioxidants are like the best "super-drug". You are countering all diseases with the same antioxidants. Unlike pharmaceuticals, where you require 1 pill for diabetes, another for heart disease, another for arthritis, etc. etc. etc.... Some antioxidants work better for certain illnesses, but for the most part, if you're getting a good range, you're pretty much covered.
Antioxidants and Skin Health Benefits
All of those toxins and radiation we're exposed to daily are major sources of free radicals. They damage your skin cells the same way they hurt your internal cells. Here's why antioxidant skin care is essential: most of the free radical damage is the outcome of radiation from the sun.
 The human body requires around 20 minutes of contact with ultraviolet sunlight for the creation of vitamin D. However, an excess amount will cause mutations to the DNA, which is a base for the formation of new cancer cells. When our skin is exposed to high levels of ultraviolet light, photo-oxidative damage is encouraged by the formation of different kinds of reactive species of oxygen, including singlet oxygen, superoxide radicals, and peroxide radicals. These forms of reactive oxygen harm cellular lipids, proteins, and DNA, and they are thought to be the primary contributors to erythema (sunburn), premature aging of the skin, photodermatoses, and skin cancers.
The human body requires around 20 minutes of contact with ultraviolet sunlight for the creation of vitamin D. However, an excess amount will cause mutations to the DNA, which is a base for the formation of new cancer cells. When our skin is exposed to high levels of ultraviolet light, photo-oxidative damage is encouraged by the formation of different kinds of reactive species of oxygen, including singlet oxygen, superoxide radicals, and peroxide radicals. These forms of reactive oxygen harm cellular lipids, proteins, and DNA, and they are thought to be the primary contributors to erythema (sunburn), premature aging of the skin, photodermatoses, and skin cancers.
Astaxanthin, followed by beta-carotene combined with vitamin E has been revealed to be one of the most potent antioxidant combinations for helping shield the skin from reactive species of oxygen. If you can get enough antioxidants in your skin cells, free radical damage would be insignificant. That would virtually stop the aging process in its tracks. Imagine!
Wrinkle fighter: antioxidants – vitamins A and C and CoQ10 in particular – wipe away those fine lines that freak us out more than a bad hair day. But in skin care, when it comes to antioxidants, the more the merrier. "Multiple antioxidants have been shown in studies to be more effective than single antioxidants," says Great Neck, New York, dermatologist Jeannette Graf, M.D., author of Stop Aging, Start Living. For example, vitamin C kicks vitamin E into a higher gear, so the two are more powerful together.
Antioxidants Provide Great Immune System Support
Antioxidants provide great Immune System Support. Boosting your immune system is pretty rough when you have continuous damage from free radicals.
There are many ways free radicals ruin your system:
- The immune cells themselves (T-cells, natural killer cells, etc) are damaged
- Next, they knock out the cytokine pathways (communication between immune cells)- they can’t function properly without communicating.
- And last, but not least, it distresses the delicate balance of free radicals that macrophages use in order to work. Macrophages actually discharge their own free radical, nitrous oxide, to destroy bacteria, parasites and viruses. If the free radical/antioxidant balance is out, the nitrous oxide ends up destroying the macrophage also.
So the best method of enhancing your immune system is to load up on free radical fighters- antioxidants!
Boosting your immune system isn't just for colds and flus. Not a lot of people know this, but improving your immune system is one of the best ways to thwart cancer too. One of the major roles of some of your immune cells is to seek out and terminate cancer cells- that way the disease never really gets going.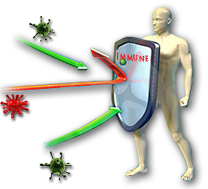
The main purpose of phytochemicals is to eradicate the cancer causing free radicals from the body. Free radicals are related with premature aging, cancer, and heart diseases. They are highly reactive and can cause severe damage to the cell walls by simply coming in contact with them. If not curbed, these free radicals can cause permanent harm to the organs of the body and may also modify the cell and gene structures.
Antioxidants are known to overpower the carcinogenic effects of free oxygen radicals. It is one of the reasons why antioxidants have remained the center of many researches related to cancers and overall health. Their conceivable roles in preventing cancers and heart diseases are still being studied. It has been found that the antioxidants accessible in herbal supplements have higher bioavailability than the antioxidants consumed through supplements in pill forms.
One of the most powerful and essential antioxidants we refer to is Glutathione. Glutathione is most famous for its general antioxidant effects. It is an amino acid sometimes called the “master antioxidant” of the human body. It accounts for a huge percentage of your total antioxidant volume.
- First and foremost, it plays a dominant role in the proper function of white blood cells, including T cell lymphocytes—the frontline soldiers of the immune system.
- Second, there is evidence that glutathione encourages the natural killing ability of immune cells.
This study defined glutathione as “a first line of defense” against oxidative stress. Other enzymes that rely on glutathione also offer a backup. To give the very short description, antioxidants help guard your cells from DNA damage that can cause serious difficulties down the line. Glutathione has more direct effects on the immune system. It is imperative for natural killer cells – “natural killer” sounds like something you don’t want in your body, but in this case the natural killers are on your side, countering viruses and bacteria that try to attack you. For instance, this study explores how glutathione affects natural killer cells (one type of immune cells) in a way that might assist fighting off tuberculosis.
Antioxidants’ Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Anytime you are feeling aches and pains, it's the result of inflammation. In fact, inflammation is what is accountable for causing just about every sickness there is. It is a direct result of the oxidative stress that free radicals cause. For example, heart disease, obesity, cancer and dementia are all associated with chronic inflammation. Worst of all, chronic inflammation may not display any symptoms until impairment and loss of function transpires.
Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation is low-grade and total. It causes damage under the radar over a lengthy period of time (typically years) until a known disease exhibits. Handling inflammation is the key to preserving one's health.
Oxidative stress is a natural byproduct of metabolic function, especially within our toxic environment. Oxidation occurs when oxygen molecules lose an electron and become damaged or unstable and morph into free radicals. A domino effect is created as the free radical tries to regain stability by stealing an electron from another molecule, and so on.
When a molecule loses an electron it's damaged. Even if the molecule steals an electron and regains stability, it's still damaged. Damaged cells create an inflammatory response that becomes chronic. These damaged cells lose functionality and eventually die.
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are the root of many age-related, chronic diseases. Chronic conditions are the cause for more than 75% of health care expenditure. Seven out of ten Americans die each year from chronic diseases, not severe infectious diseases. A CDC statistic showed one out of every two adults had at least one chronic disorder.
A 2009 Russian study with mice confirmed that naturally occurring fat soluble antioxidants lessen inflammation. Fifteen days before artificially induced with acute inflammation, the experimental/treatment group was given fat soluble antioxidants: Coenzyme Q9, Coenzyme Q10, Alpha-Tocopherol, Vitamin E, Beta-Carotene15. The control group of mice was not given any antioxidant. The researchers determined that unique antioxidant combinations could be used therapeutically to decrease the inflammatory response and act as a catalyst for the immune system.
Antioxidants break the inflammation process at various stages. So whether you just injured yourself, or you have chronic inflammation, like arthritis, antioxidants can still be beneficial.
So the natural anti-inflammatory effects that antioxidants have are actually part of the whole "disease prevention" benefit. They impede the different steps of the inflammatory process.
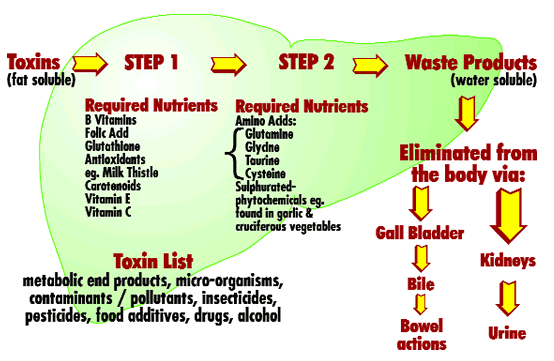
Antioxidants Detoxification Benefits
And again comes Glutathione.
Glutathione is critical for purification in the liver; unlike some other detoxification schemes that will remain nameless, it actually has documented evidence of an advantage. It’s also necessary for healthy immune function and general antioxidant defenses against free radicals.
Glutathione supports the function of your liver, kidneys, GI tract and intestines—your body’s major detoxification pathways. Glutathione helps in two main ways:
- it aids in removing toxins and consumed chemicals that the body has already absorbed
- it interrupts and nullifies toxins in the GI tract before they are even absorbed
In the liver, glutathione attaches to toxins before they’re excreted, which is an essential step in getting them out of your body. In fact, the detox power of glutathione is so potent that it’s used for people who overdose on Tylenol (acetaminophen) and have to go to the hospital in order to detox. In that case, the person receives an IV with another amino acid that enables their body make glutathione, called N-acetyl cysteine (NAC). The NAC escalates their body’s production of glutathione, which helps their liver get rid of the acetaminophen.
Glutathione may also be central for helping your body get rid of toxins in your food and environment. For example, one study established that in people who eat a lot of fish, the total quantity of mercury the people reserved in their bodies was related to genes regulating glutathione synthesis. The more glutathione people produced, the less mercury they retained.
Another natural antioxidant is curcumin. Curcumin is a harmless and nutritious component in food that is not only a highly effective antioxidant, but has been shown to engage in protective roles against mercury in the body as well as glutathione.
Antioxidants’ Anti-Aging Benefits
Antioxidant anti-aging benefits have also been verified scientifically. Laboratory experiments on cells have shown that antioxidants may help stand against oxidative stress and offer anti-aging benefits. What’s more, data from population studies show that people with a higher intake of antioxidant-rich vegetables and fruits may have a lower chance of contracting some chronic diseases linked to aging. There's some proof that antioxidants may help defend against age-related macular degeneration (one of the leading causes of blindness in the United States).
In a clinical trial published in 2001, researchers monitored 3,640 participants with age-related macular degeneration for an average of 6.3 years. Results showed that those who took a blend of antioxidants and zinc in supplement form had a 25 percent reduced risk of developing advanced stages of age-related macular degeneration (compared to those assigned to a placebo).
Think of all the symptoms you would typically associate with aging—declined mobility, mental function, aches and pains, wrinkles...you name it. Now think of any illness— heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, cancer, Alzheimer's, Multiple Sclerosis... just about any disease you can think of.
Scientific studies now show that all of those symptoms we usually associate with aging, as well as just about every disease there is, are caused by the harm of free radicals on your body.
By combating free radicals, antioxidants are thought to battle oxidative stress (and, in turn, create an anti-aging effect). The symptoms that you generally associate with aging are also the outcome of amassed damage from free radicals to your cells.
So if you can prevent this damage... Voila! You can slow the effects of aging.
You may also like:
Free Radicals: Enemies Within. What Are They And How Are They Formed
Understanding Antioxidants. How Do They Work?
How You Can Rate The Best Antioxidant? Is ORAC Score A Useful Tool?
How Can We Recognize Antioxidant Rich Food?
The Most Common Sources Of Antioxidants
Classification Of The AntiOxidants