Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, which plays a role as an antioxidant in the body. It also helps to prevent free radical damage to specific fats in the body that are critical for your health. Vitamin E is an important vitamin that is required for the proper function of many organs in the body and is extremely useful in naturally slowing aging. It is found in many foods including certain oils, nuts, poultry, eggs, fruits and wheat germ oil. It is also available as a supplement. Vitamin E benefits include treating and preventing diseases of the heart and blood vessels; such as chest pains, high blood pressure, and blocked or hardened arteries. (1)
Top 10 Vitamin E Benefits
Supplementing and consuming vitamin E rich foods have the following health benefits:
1. Balances Cholesterol
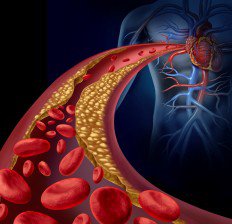 Cholesterol is a naturally occurring substance made by the liver and required by the body for the proper function of your cells, nerves, and hormones. When cholesterol levels are in their natural state, they are balanced, normal and healthy. When it oxidizes, it becomes dangerous. Studies have shown that Vitamin E serves as a protective antioxidant that fights cholesterol oxidation (2). This is because vitamin E can fight free radical damage in the body, which leads to cholesterol oxidation.
Cholesterol is a naturally occurring substance made by the liver and required by the body for the proper function of your cells, nerves, and hormones. When cholesterol levels are in their natural state, they are balanced, normal and healthy. When it oxidizes, it becomes dangerous. Studies have shown that Vitamin E serves as a protective antioxidant that fights cholesterol oxidation (2). This is because vitamin E can fight free radical damage in the body, which leads to cholesterol oxidation.
2. Fights Free Radicals and Prevents Disease Development
Free radicals fight and break down the healthy cells in your body and this can lead to heart disease and cancer. These molecules form naturally in your body and they can cause severe damage when they accelerate or oxidize. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that has the power to reduce free radical damage, fight inflammation, and therefore to help to naturally slow aging in your cells and fight off health issues like heart disease (3). Studies have shown that Vitamin E can significantly increase immunity, therefore helping to prevent both common illnesses and serious conditions from forming (4).
3. Repairs Damaged Skin
Vitamin E helps to strengthen the capillary walls in your skin and to improve moisture and elasticity, acting as a natural anti aging nutrient within your body. Studies have shown that Vitamin E helps to reduce inflammation both within your body and on your skin, helping to maintain healthy, youthful skin (5). These antioxidant properties are also helpful when you are exposed to cigarette smoke or ultraviolet rays from sunlight, protecting against skin cancer. Taking vitamin E with vitamin C fights skin inflammation after exposure to UV radiation and can also be useful in decreasing signs of acne and eczema. Vitamin E also helps the healing process in the skin. It is absorbed by the epidermis layer of the skin and can be used to treat sunburn, which is one of the leading causes of skin cancer among other factors. Because it speeds up cell regeneration, it can be used to treat scars, acne, and wrinkles; this makes your skin look healthier and younger.
4. Thickens Hair
 Because Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant, it helps to decrease environmental damage to your hair. It can also promote circulation to the scalp. Vitamin E oil can retain the natural moisture in your skin, which will help your scalp from becoming dry and flakey. This oil will also make your hair look healthier and fresher. You can apply a few drops of vitamin E oil on your hair, especially if it is looking dry and dull.
Because Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant, it helps to decrease environmental damage to your hair. It can also promote circulation to the scalp. Vitamin E oil can retain the natural moisture in your skin, which will help your scalp from becoming dry and flakey. This oil will also make your hair look healthier and fresher. You can apply a few drops of vitamin E oil on your hair, especially if it is looking dry and dull.
5. Balances Hormones
Vitamin E can help to play a crucial role in balancing your endocrine and nervous system, naturally working to help keep your hormones balanced (6). Symptoms of a hormonal imbalance may include PMS, weight gain, allergies, urinary tract infections, changes in the skin, anxiety, and fatigue. By keeping your hormones in balance, you will find it easier to maintain a healthy weight, you will keep a regular menstrual cycle, and you will find yourself feeling more energetic.
6. Helps PMS Symptoms
Taking a vitamin E supplement 2-3 days before and 2-3 days after a menstrual period can reduce the cramping, anxiety, and cravings that are related to PMS. Vitamin E can decrease pain severity and duration, and it can reduce menstrual blood loss. It does this by balancing your hormones naturally and it helps to keep your menstrual cycle regulated.
7. Improves Vision
 Vitamin E may help decrease the risk of age-related macular degeneration, which is a common cause of blindness. Keep in mind, in order for vitamin E to be effective for vision, it must also be consumed with adequate intakes of vitamin C, beta carotene, and zinc. It has also been found that taking high doses of vitamin E and vitamin A daily seems to improve healing and vision in people undergoing laser eye surgery.
Vitamin E may help decrease the risk of age-related macular degeneration, which is a common cause of blindness. Keep in mind, in order for vitamin E to be effective for vision, it must also be consumed with adequate intakes of vitamin C, beta carotene, and zinc. It has also been found that taking high doses of vitamin E and vitamin A daily seems to improve healing and vision in people undergoing laser eye surgery.
8. Helps People with Alzheimer’s Disease
Vitamin E may slow down the worsening of memory loss and functional decline in people with moderately severe Alzheimer’s disease. It may also delay the loss of independence and the need for a caregiver or assistance. Vitamin E, taken with Vitamin C, can also decrease the risk of developing several forms of dementia (7).
9. Improves Effects of Medical Treatments
Vitamin E is sometimes used to lessen the harmful effects of medical treatments such as radiation and dialysis. This is because it is a powerful antioxidant that fights off free radicals in the body. It is also used to reduce unwanted side effects of drugs that may cause hair loss of lung damage.
10. Improves Physical Endurance and Muscle Strength
 Vitamin E can be used to improve your physical endurance. It can increase your energy and reduce the level of oxidative stress on your muscles after you exercise (8). Vitamin E can also improve your muscle strength. Vitamin E eliminates fatigue by promoting blood circulation; it can also strengthen your capillary walls and nourish your cells.
Vitamin E can be used to improve your physical endurance. It can increase your energy and reduce the level of oxidative stress on your muscles after you exercise (8). Vitamin E can also improve your muscle strength. Vitamin E eliminates fatigue by promoting blood circulation; it can also strengthen your capillary walls and nourish your cells.
Vitamin E Sources
According to the USDA, the RDA for vitamin E is 15 mg/day (22.5 IU). I recommend consuming 2-3 of these vitamin E rich foods daily:
- Sunflower seeds
1 cup: 33.41 mg (220%) - Almonds
1 cup: 32.98 mg (218%) - Hazelnuts
1 cup: 20.29 mg (133%) - Wheat Germ
1 cup plain, uncooked: 18 mg (120%) - Mango
1 whole raw: 3.02 mg (20%) - Avocado
One whole raw: 2.68 mg (18%) - Butternut Squash
1 cup cooked and cubed squash: 2.64 mg (17%) - Broccoli
1 cup cooked: 2.4 (12%) - Spinach
½ cup cooked or about 2 cups uncooked: 1.9 mg (10%) - Kiwi
1 medium: 1.1 mg (6%) - Tomato
1 raw: 0.7 (4%)

If you are looking to increase the amount of vitamin E that you are consuming in a day, get creative using these foods! Add nuts or seeds to your cereal, oatmeal, or salad. You can also snack on nuts or make your own granola. Add a boost of vitamin E to your lunch or dinner by having a spinach or kale salad; add in tomatoes, shrimp, tofu, or even fresh fruit like papaya. If you are looking to have a healthy, vitamin E heavy snack, try a sliced apple with peanut butter, or smashed avocado on toast. An easy way to get some vitamin E in your diet is to add just a tablespoon of wheat germ oil to any recipe. It can be fun to mix up these food options and experiment with healthy- vitamin rich meals.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin E
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) includes the vitamin E that you get from both the food that you eat and any supplements you take. The daily intake is measured in milligrams (mg) and international units (IU).
Children:
1 – 3 years: 6 mg/day (9 IU) 
4 – 8 years: 7 mg/day (10.4 IU)
9 – 13 years: 11 mg/day (16.4 IU)
Females:
14 years and up: 15 mg/day (22.4 IU)
Pregnant: 15 mg/day (22.4 IU)
Breastfeeding: 19 mg/day (28.5 IU)
Males:
14 years and up: 15 mg/day (22.4 IU)
The tolerable upper intake levels are the highest amount of a vitamin that most people can take safely (9). These high doses can be used to treat a vitamin E deficiency, and it is important to speak to a doctor before taking more than these upper intake levels.
1 – 3 years: 200 mg/day (300 IU)
4 – 8 years: 300 mg/day (450 IU)
9 – 13 years: 600 mg/day (900 IU)
14 – 18 years: 800 mg/day (1,200 IU)
18 years and up: 1,000 mg/day (1,500 IU)
Keep in mind that because vitamin E is fat-soluble, supplements work best when they are absorbed with food, and the American Heart Association recommends obtaining antioxidants, including vitamin E, by eating a healthy and well-balanced diet that is high in fruits, veggies, and whole grains. Getting your vitamins from the food you eat is always a better alternative than using a supplement because it is difficult to over-consume vitamin E when getting it from your regular diet.
Keep in mind that because vitamin E is fat-soluble, supplements work best when they are absorbed with food, and the American Heart Association recommends obtaining antioxidants, including vitamin E, by eating a healthy and well-balanced diet that is high in fruits, veggies, and whole grains. Getting your vitamins from the food you eat is always a better alternative than using a supplement because it is difficult to over-consume vitamin E when getting it from your regular diet.
Vitamin E Deficiency Symptoms
Vitamin E deficiencies are rare and it is almost never caused by a poor diet. There are specific situations that may lead to a vitamin E deficiency. A premature infant who is born weighing less than 3.5 pounds is in danger of a vitamin E deficiency. but a pediatrician who specializes in the care of newborns will typically evaluate the nutritional needs of an infant. People with fat absorption problems, which is a common problem for those who struggle with inflammatory bowel disease, may struggle with a deficiency.
People who have an issue with their dietary fat levels are also at risk because this is needed for the absorption of vitamin E. This includes anyone who has been diagnosed with cystic fibrosis, has had a gastric bypass, or people with malabsorption problems such as Crohn’s disease, liver disease, or pancreatic insufficiency. Deficiency symptoms include loss of muscle coordination, and impaired vision and speech.
Vitamin E Side Effects
Vitamin E benefits most healthy people when taken by mouth or applied to the skin. Most people will not experience any side effects when taking the recommended dose. Vitamin E may be unsafe when taken in high doses, especially for people who have conditions such as heart disease or diabetes. If you suffer from these health issues, do not take doses of 400 IU/day or more.
Some studies show that taking high doses of vitamin E, which is between 300-800 IU each day, might increase the chance of having a serious stroke called hemorrhagic stroke by 22%. One serious side effect of too much vitamin E is an increased risk of bleeding, especially in the brain.
Avoid taking supplements containing vitamin E or any other antioxidant vitamins immediately before and following angioplasty, a heart procedure. These vitamins seem to interfere with proper healing, so speak to your health care professional if you are undergoing this kind of procedure.
Supplementing with very levels of Vitamin E could potentially lead to the following health concerns:
- heart failure in people with diabetes
- worsening bleeding disorders
- increasing the chances that head, neck, and prostate cancer will return
- increasing bleeding during and after surgery
- increasing chance of death after a heart attack or stroke
One study found that vitamin E supplements can be harmful to women who are in the early stages of pregnancy. Women that took vitamin E supplements during their first 8 weeks of pregnancy showed an increase of congenital heart defects. (10)
High doses of vitamin E can also lead to nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps, fatigue, weakness, headache, blurred vision, rash, bruising, and bleeding. Topical vitamin E can irritate some people’s skin, so try a small amount first and make sure you don’t have a sensitivity.
Relationship With Other Nutrients and Interactions
Vitamin E supplements can slow down blood clotting, and when you are using medications that also slow clotting, you may increase the chances of bruising and bleeding. Some medications that slow blood clotting include aspirin, clopidogrel, ibuprofen, and warfarin. Warfarin (Coumadin), in particular, is used to slow blood clotting. Taking vitamin E with warfarin can increase your chances of bruising and bleeding, so be sure to have your blood checked regularly in order to regulate your dosing.
Medications that are used for lowing cholesterol may also interact with vitamin E. It is not known if taking vitamin E alone decreases the effectiveness of some medications that are used for lowing cholesterol, but it does seem to affect your cholesterol when taken with beta-carotene, vitamin C, and selenium.
- Check the brand that I personally use and recommend:
Forever A-Beta Carotene (with selenium) and Absorbent C
with Olive Oil and Omega Fish Oil
=> Omega Arctic Sea - All 3 in ONE Omega
Also if you want to use vitamin E only check this brand => Deva's Vegan Natural Source Vitamin E with Mixed Tocopherols is a potent antioxidant supplement that can help protect the cells of the body from the oxidative damage of free radicals. This non-GMO supplement provides 400 IU of vitamin E as well as d-gamma, d-beta and d-delta tocopherols for added antioxidant support.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0003058/
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15061748
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16011463
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10714244
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7633944
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15753140
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24381967
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10701711
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0003058
http://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/lifestyle-guide-11/supplement-guide-vitamin-e?page=2
You may also like:
Understanding Antioxidants. How Do They Work?
The Most Common Sources Of Antioxidants





